Lack of Capital Business Definition
What is Capital?
Capital is anything that increases one's ability to generate value. It can be used to increase value across a wide range of categories, such as financial, social, physical, intellectual Interpersonal Skills Interpersonal skills are the skills required to effectively communicate, interact, and work with individuals and groups. , etc. In business and economics, the two most common types of capital are financial and human. This guide will explore all the above categories in more detail.
Types of Capital
The different types of capital include:
1. Financial
- Equity Stockholders Equity Stockholders Equity (also known as Shareholders Equity) is an account on a company's balance sheet that consists of share capital plus
- Debt Senior and Subordinated Debt In order to understand senior and subordinated debt, we must first review the capital stack. Capital stack ranks the priority of different sources of financing. Senior and subordinated debt refer to their rank in a company's capital stack. In the event of a liquidation, senior debt is paid out first
- Investments
- Working capital
2. Human
- Social Emotional Intelligence Emotional intelligence also known as the emotional quotient (EQ) is the ability to manage one's emotions and the emotions of others. For
- Intellectual
- Physical
- Talents/skills
3. Natural
- Commodities
- Animals
- Vegetation
- Ecologies
Capital in Business
The focus of this guide is on capital in a business context, which can include all three of the broad categories above (financial, human, natural). Let's explore each of the categories in more detail.

1. Financial
The most common forms of financial capital are debt and equity.
Debt is a loan or financial obligation that must be repaid in the future. It has an interest expense attached to it, which is the cost of borrowing money. The cash received from borrowing money is then used to purchase an asset and fund the operations of a business, which in turn generates revenues for a company.
Equity is an ownership stake in a company, and equity investors will receive the residual value of the company in the event it is sold or wound-down. Unlike debt, it does not have to be repaid and doesn't have an interest expense associated with it. Equity is used to fund the business and purchase assets to generate revenue.
2. Human
Human capital is used by businesses to create products and perform services that can be used to generate revenue for the company. Companies don't "own" people they way they do other assets. The most common types of human capital are intellectual and skills/talents.
Intellectual refers to the intelligence of people, which can be used to successfully run a company, think creatively, solve problems, form strategies, and outperform competitors.
Skills and talents are used in much the same way as intelligence to help a business operate and generate revenues. Skills do not necessarily require mental capacity and can include manual labor, physical exertion, social influence, etc.
3. Natural
Natural capital can also be used by businesses to generate income and increase production. Many businesses use natural resources such as water, wind, solar, animals, trees, plants, and crops to operate their company and increase value over time.
Companies may or may not own the natural assets they require to operate.
Cost of Capital
In a financial context, there is an associated cost of acquiring capital to run a company.
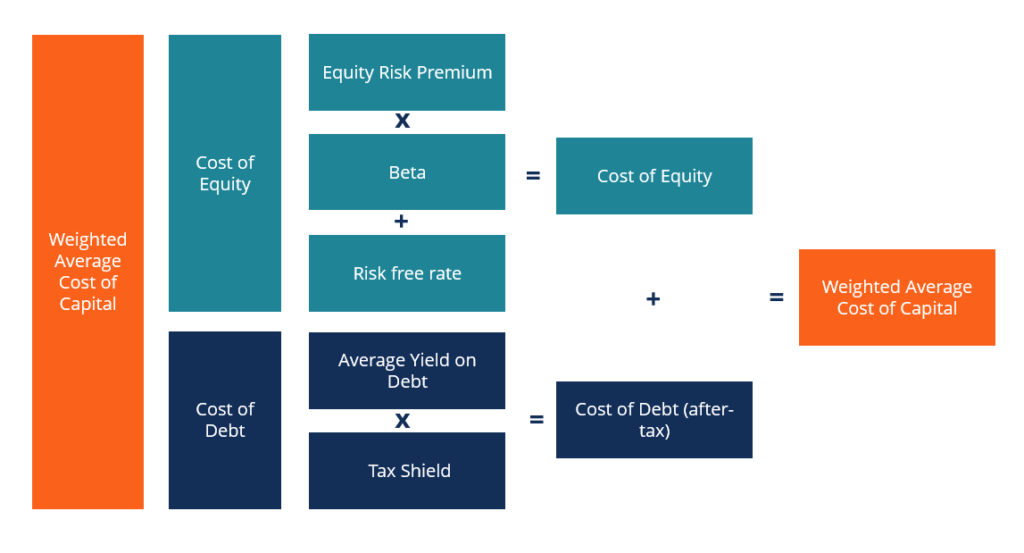
The cost of debt is based on the coupon, interest rate Interest Rate An interest rate refers to the amount charged by a lender to a borrower for any form of debt given, generally expressed as a percentage of the principal. , and yield to maturity of the debt. For example, if a company borrows $5 million and must pay $0.5 million in annual interest, it's cost of debt would be 10%.
Since the interest expense is tax-deductible, the after-tax cost of debt is equal to the interest rate multiplied by one minus the tax rate. Continuing with the example above, if the company's tax rate is 25%, the after-tax cost of debt would be 10% x (1 – 25%) = 7.5%.
The cost of equity is an implied cost that is calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a model that describes the relationship between expected return and risk of a security. CAPM formula shows the return of a security is equal to the risk-free return plus a risk premium, based on the beta of that security , which uses the riskiness of an investment (the volatility of its returns) as a means of determining how much it should cost per year. The cost of equity is always higher than the cost of debt because it carries more risk (in the event of insolvency, debt is repaid before equity). To learn more, read CFI's guide to the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) WACC WACC is a firm's Weighted Average Cost of Capital and represents its blended cost of capital including equity and debt. .
Importance in Business
In business, a company's capital base is absolutely essential to its operation. Without adequate funding, a company may not be able to afford the assets it needs to operate and survive, nor be able to outperform its competitors. Financial analysts perform extensive analysis to assess how well funded a business is, how efficient its operation is, and how good a job it does of generating a return for the investors who fund the business.
Managers and operators of a business are typically very focused on being efficient in operations and generating the highest possible returns for their investors. Common examples of metrics and financial ratios managers and analysts look at to measure the performance of a company include:
- Return on Assets (ROA) Return on Assets & ROA Formula ROA Formula. Return on Assets (ROA) is a type of return on investment (ROI) metric that measures the profitability of a business in relation to its total assets.
- Return on Equity (ROE) Return on Equity (ROE) Return on Equity (ROE) is a measure of a company's profitability that takes a company's annual return (net income) divided by the value of its total shareholders' equity (i.e. 12%). ROE combines the income statement and the balance sheet as the net income or profit is compared to the shareholders' equity.
- Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) ROIC ROIC stands for Return on Invested Capital and is a profitability ratio that aims to measure the percentage return that a company earns on invested capital.
Money vs. Capital
While money (currency) and capital may seem like the same thing, they are not. Capital is a much broader term that includes all aspects of a business that can be used to generate revenue and income, i.e., the company's people, investments, patents, trademarks, and other resources.
Money is what's used to complete the purchase or sale of assets that the company employs to increase its value.

Additional Resources
Thank you for reading this guide on capital; we hope it has been helpful.
CFI is the official global provider of the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)TM Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst. To continue advancing your career, these additional CFI resources will be helpful:
- Capitalism Capitalism Capitalism is an economic system that allows for and encourages the private ownership of businesses that operate to generate profit. Also
- Income statement Income Statement The Income Statement is one of a company's core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time. The profit or
- Cash flow statement Cash Flow Statement A cash flow Statement contains information on how much cash a company generated and used during a given period.
- Guide to financial modeling What is Financial Modeling Financial modeling is performed in Excel to forecast a company's financial performance. Overview of what is financial modeling, how & why to build a model.
Lack of Capital Business Definition
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/capital/
0 Response to "Lack of Capital Business Definition"
Enviar um comentário